Guide to Representing Yourself on Appeal
To download this guide as a PDF click here.
Introduction
THE PURPOSE OF THIS GUIDE
This guide is designed to assist anyone filing an appeal in the First District Court of Appeals. Proceedings in this Court must comply with the Ohio Rules of
Appellate Procedure and the First District’s local rules. This guide is not legal authority or a substitute for those rules and is not intended to provide legal advice. The rules are available on this Court’s website at https://www.firstdistrictcoa.org

Who We Are
The First District Court of Appeals is located in Hamilton County, Ohio. We hear appeals from all divisions of the Hamilton County Court of Common Pleas, including
General Division, Domestic Relations, and Probate, as well as appeals from the Hamilton County Municipal Court and the Hamilton County Juvenile Court. Six judges serve on the Court. An appeal is decided by a panel of three judges.
What We Do
When an appeal is filed, the Court of Appeals does not “retry” a case or consider new evidence. We review what happened in the trial court and decide whether an
error occurred and, if so, whether that error requires us to reverse or modify the judgment appealed. The court of appeals decides an appeal based on the record created in the trial court, the assignments of error and arguments presented in the briefs filed by the parties to the appeal, and oral argument, if any, before the Court.
In some actions, the First District is the court of original jurisdiction. These actions are generally referred to as original actions. In these cases, the Court may accept evidence.
WHERE WE ARE
The administrative office and courtrooms for the First District Court of Appeals are located at:
230 East Ninth Street, 12th Floor
Cincinnati, Ohio 45202
Phone: 513-946-3500
The office is open Monday through Friday, from 8:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m
SELF-REPRESENTATION (“PRO SE”)
If you are not an attorney, you can represent yourself (but not others) in a case before the Court of Appeals. Parties who represent themselves must comply with all applicable rules and laws. Failure to comply may result in dismissal of your appeal or some other sanction.
CHANGE OF NAME OR ADDRESS
It is important that you immediately contact the Court concerning any change of name, e-mail, or mailing address.
CONTACT US
If you have questions, please call the court at (513) 946-3500, between 8:00 a.m. and 4:00 p.m. Court employees can answer general procedural questions, but they cannot give you legal advice.
.
Structure of the Ohio Judicial System
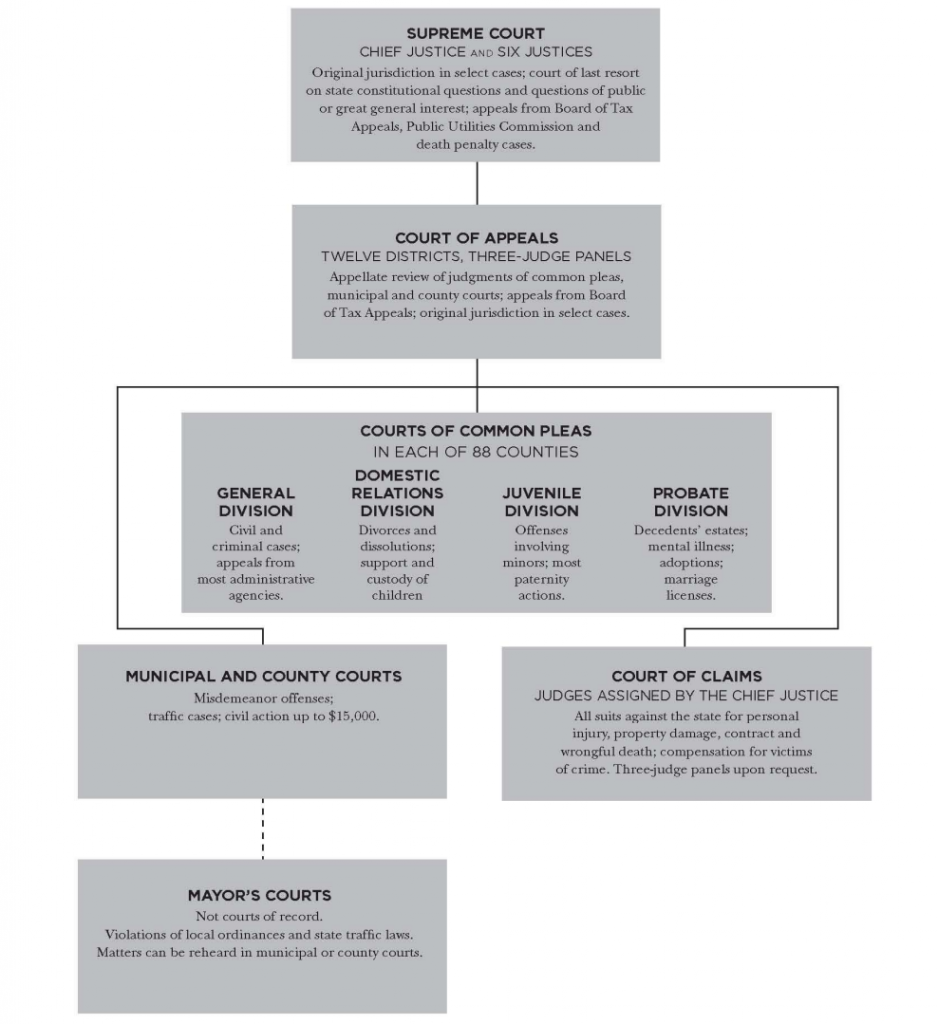
*Note: In Hamilton County, the juvenile court is a separate court, known as the Hamilton County Juvenile Court and is not division of the Court of Common Pleas
The Steps in an Appeal

Serving and Filing Documents
After the notice of appeal is filed, a document may be filed with the First District Court of Appeals, either by e-filing, delivering the document in person, or by mailing. For in-person filing, the Clerk’s Office is open on Monday through Friday from 8:00 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. The mailing address is:
William Howard Taft Law Center
230 East Ninth Street, 12th Floor
Cincinnati, Ohio 45202
To e-file visit: https://www.courtclerk.org/forms-filings/e-filing/ or you may access e-file portal through the court’s website located at www.firstdistrictcoa.org.
For more information on filing documents, visit the “E-Filing Guide” located on the court’s website at www.firstdistrictcoa.org
The cover page of the document must bear the caption:
FIRST APPELLATE DISTRICT OF OHIO
HAMILTON COUNTY, OHIO
and include the case title and number and a descriptive title indicating the purpose of the document. App.R. 19(A).
An original plus one copy of any motion or brief must be filed, unless the brief is e-filed.
Loc.R. 18.
The party who files a document with the Court must, on or before the day of filing, serve the document on all other parties to the appeal as set forth in App.R. 13(C), Loc.R. 13.1(C).
Proof of service may be either included in the document or provided separately and must be provided in the form of a certified statement by the person who served the document, specifying the person served and the date and manner of service:
CERTIFICATE OF SERVICE

How to file a document
A document may be filed with the Hamilton County Clerk of Courts by presenting the document in person, by United States mail, by e-filing, or by any other means provided by App.R. 13(A) and Loc.R. 13.1.
To e-file a document, register for e-filing at: https://cmsnet.hamiltoncountycourts.org/CourtClerkEfiling/registration.aspxgo. You may also access the e-filing portal on the Court’s website at www.firstdistrictcoa.org.
How to serve a document
A document is served by presenting it in person, by United States mail, or by any other means provided by App.R. 13(C). If a party is represented by counsel, service must be on counsel, and not the party. App.R. 13; Loc.R. 13.1.
Personal identifying information in a document filed with the court
Documents filed with the Court are available to the public on the internet through the Clerk of Court’s website or through the Clerk of Courts office. To protect a person’s identity and privacy, certain personal and private information must be removed from or blacked out on those documents before you file them. This information includes, but is not limited to the following:
- Social security number or other personal identifier
- Name of a minor child
- Name of a victim of a sex offense
- Financial-account number
- Other information deemed personal and private by a federal or state constitution, statute, regulation, executive order, or court ruling, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act.
For more information as to what information must be redacted from filings, refer to Loc.R.13.2 and the Ohio Rules of Superintendence R. 44(H) and 45(D).
Where personal or private information is redacted, a party should complete and file a Personal Identifier Form, Form 13.2.
Filing the Appeal
What judgments may be appealed?
The Court of appeals has jurisdiction to review a final appealable order entered by a trial court or by certain administrative agencies. An order that decides the whole case, such as a judgment of conviction in a criminal case, is generally final and appealable. Some orders that decide only part of a case may be appealable, but that grant of jurisdiction involves substantive legal questions beyond the scope of this guide.
What is a stay?
Filing a notice of appeal does not stop the judgment appealed from going into effect. A stay is an order that puts the judgment appealed on hold until the Court of Appeals decides the appeal. These requests are governed by App.R. 7 and Loc.R 4.1 for civil cases and App.R. 8 and Loc.R. 4.2 for criminal cases.
A motion for a stay must ordinarily be filed first in the trial court. If the trial court denies the motion, then the motion may be filed in the Court of Appeals. App.R. 7 and 8; Loc.R. 4.1 and 4.2. Funds in the form of cash, property, bonds, or other appropriate security may be required to secure a stay.
See Form 7 for more information.
How is an appeal filed?
Within 30 days after a final appealable order is entered, the appellant must:
- file a notice of appeal and docket statement and pay the filing fee, unless waived
- order the record, including transcript of proceedings
After 30 days, an appellant may file a motion for leave to file a delayed appeal from a judgment in a criminal, delinquency, or serious-youthful-offender proceeding.
What if the appellant is indigent?
Waiver of Filing Fee
The filing fee must be paid for the clerk to accept the notice of appeal. The filing fee may be waived for an indigent appellant who is unable pay the fee and can prove that fact. The fee may be waived by completing and filing with the notice of appeal the appropriate form:
- Form 20 Civil Fee Waiver Affidavit and Order form – When an indigent appellant files this form in an appeal from a judgment entered in a civil division of the municipal or common pleas court, the Clerk will accept the notice of appeal without the fee. The Court will then review the application. If the 10 Court finds that the appellant is indigent, the Court will order the Clerk to waive prepayment of the court costs related to the appeal. If the Court finds that the appellant is not indigent, the appellant must pay the fee, or the appeal will be dismissed. R.C. 2323.311.
- Form 3.1NCR Indigent.1 Affidavit of Indigency – Filing this form may waive the fee for an indigent appellant in an appeal from a conviction entered in a criminal case or a judgment entered in juvenile court in a dependency, abuse, or neglect case, or in a child-support contempt case when the party may be jailed. There is no fee for filing an appeal from a judgment entered in juvenile court in a delinquency case.
Appointment of Counsel and Transcript of Proceedings at State Expense
In an appeal from a criminal conviction, certain probate-court judgments, or most juvenile-court judgments (excluding a private child-custody case), the following forms, along with an entry for a judge to sign, may be filed by an indigent appellant:
- Form 3.4 Motion to Appoint Counsel, requesting the appointment of counsel for the appeal and indicating that appellant cannot afford appellate counsel.
- Form 9 Motion to Prepare Transcript of Proceedings at State Expense, stating that the appellant is indigent and unable to pay for a transcript of the proceedings leading to the judgment appealed.
Notice of Appeal
Filing the notice of appeal initiates the case with the Court of Appeals.
When multiple parties to a case have a right to appeal, the parties may file a joint notice of appeal or the parties may file their own separate notices of appeal. App.R. 3(B). A notice of cross-appeal may be filed by a party to the action whose interests are not the same as the first appellant’s interests, but who still wishes to reverse or modify the trial court’s judgment.
See App.R. 3(C) for further guidance when a notice of cross-appeal may be appropriate
Where is the notice of appeal filed?
A notice of appeal must generally be filed with the clerk of the trial court. See Chart 1, for more details.
24-Hour Filing
A notice of appeal from a judgment entered in a municipal, common pleas (general division), and domestic-relations-court case may be filed at any time at 1000 Sycamore Street, Cincinnati, Ohio 45202 or by e-filing. See Chart 1 for details.
What must be included in the notice of appeal?
A notice of appeal must contain:
- Heading indicating the court in which the appeal is filed;
- Name of each party to the appeal;
- Statement that the appeal is to the Court of Appeals, First Appellate District of Ohio;
- Description of the judgment appealed;
- Court that entered that judgement;
- Date that judgment was entered;
- Contact information required by Loc.R. 3.2 for the appellant’s lawyer or the appellant, if not represented by a lawyer;
- Contact information required by Loc.R. 3.2 for any party served with the notice of appeal or that party’s lawyer;
- Certificate of service, certifying that the notice of appeal was served and the method of service on the Prosecuting Attorney in a criminal appeal or on each appellee or each appellee’s lawyer in a civil appeal.
- A copy of the order or judgment appealed from must be attached.
App.R. 3(A) and (D); Loc.R. 3.1.
Form 3.1NCR Notice of Appeal-Criminal
Form 3.1NCV Notice of Appeal-Civil
When must the notice of appeal be filed?
The notice of appeal must be filed within 30 days from the date that the judgment appealed is entered by the clerk of the trial court. App.R. 4(A).
Holidays and weekends count toward the 30 days. But if the final day falls on a holiday or weekend, then the notice of appeal may be filed on the next business day. App.R. 14(A).
The time for filing a notice of appeal may not be extended by the trial court or court of appeals. App.R. 14(B).
Exceptions to the 30-day rule are provided under App.R. 4(B) and include
- A notice of cross-appeal may be filed either within 30 days after the judgment was entered or within 10 days after the first notice of appeal was filed, whichever is later. App.R. 4(B)(1).
- The notice of appeal may be filed within 30 days after the trial court enters an order deciding certain timely filed and appropriate post-judgment motions, objections, or requests. App.R. 4(B)(2) and (B)(3).
NOTE: If the notice of appeal is not filed within 30 days after the judgment is filed, and no exception applies, the court of appeals will dismiss the appeal for lack of
jurisdiction.
When the appellant has failed to timely appeal a judgment of conviction in a criminal case or a judgment in a delinquency or serious-youthful-offender proceeding, a motion for delayed appeal may be filed. The Motion for Leave to File a Delayed Appeal, along with a copy of the notice of appeal, must be filed with the clerk of the court of appeals. If leave is granted, the appeal will proceed as a timely filed appeal. App.R. 5(A). A notice of appeal must also be filed in the trial court case at the same time the motion for leave is filed with the court of appeals. Form 5.
Docket Statement
Along with the notice of appeal, the appellant must file two copies of the appropriate docket-statement form. Appellant must also serve a copy of the docket statement on appellee’s counsel or on the appellee if unrepresented. Loc.R. 3.1(B) and (C).
Form 3.1DCR Criminal Docket Statement must be filed in an appeal from a judgment of conviction in a criminal case, a juvenile-delinquency adjudication, or the denial of postconviction relief. App.R. 3(G); Loc.R. 3.2(A)(2)(a).
Form 3.1DCV Civil Docket Statement must be filed in an appeal from a judgment in a civil case. App.R. 3(G); Loc.R. 3.2(A)(2)(b).
If a transcript of proceedings will be included as part of the record on appeal, a court reporter’s certification must be included in the docket statement. App.R. 9(B); Loc.R. 3.1DCR; Loc.R. 3.1DCV. The court reporter must indicate if the transcript will be ready for filing within 40 days (or in some instances 20 days) of the filing of the notice of appeal. If the transcripts will not be completed and filed in this timeframe, the court reporter must explain why and provide the date the transcript will be ready for filing. See Form 3.1DCR/3.1DCV. For details on where to go to get the court reporter’s certification for the docket statement, see Chart 2.
A show-cause order will be issued by the Court of Appeals if an appellant has not timely filed a complete docket statement. If the appellant does not comply with the order, the appeal may be dismissed. App.R. 3(G); Loc.R. 3.2(C)
Record on Appeal
The record on appeal consists of
- Original papers and exhibits to those papers filed in the trial court;
- Transcript of the proceedings, including exhibits;
- Certified copy of the docket and journal entries;
App.R. 9(A).
In some limited circumstances, the parties may agree that a transcript is not necessary and the parties can agree to the facts and conclusions of law below:
An agreed statement of the case may be filed by the parties with the trial court in place of the transcript of proceedings on appeal. App.R. 9(D); Loc.R. 3.1DCR; Loc.R. 3.1DCV.
What if the existing record on appeal is incomplete?
Depending on why the record is incomplete, the appellate rules provide some options to ensure the Court of Appeals has a complete record to decide the case.
A motion to supplement the record on appeal may be filed with the trial court or the court of appeals to correct an omission or misstatement concerning whether the record truly discloses what occurred before the trial court. App.R. 9(E).
If a transcript of the proceeding was not created, unavailable, or was lost:
A statement of the evidence or proceedings may be filed with the trial court and served on the appellee, if a recording of the proceedings before the trial court is not available.
App.R. 9(C).
What is the transcript of the docket and journal entries?
The transcript of the docket and journal entries consists of the original papers and entries filed in the trial court, assembled in the order filed, numbered, and certified to the Court of Appeals by the clerk of courts. This numbered sheet is filed with the Court of Appeals and is what should be cited in a party’s brief. Loc.R. 16.1(D).
What is the transcript of proceedings?
A transcript of proceedings provides the written record of what happened at trial or at a hearing during the proceedings leading to the judgment appealed. A transcript of proceedings that complies with App.R. 9(B)(6) must be provided to the court of appeals, when the appellant claims that an error occurred during those proceedings, and that claim of error depends for its resolution on that transcript. App.R. 9(B)(1).
How is a transcript of proceedings ordered?
The appellant is responsible for making sure that the parts of the proceedings that the appellant considers necessary to the appeal are transcribed, and that the transcript of proceedings is included in the record on appeal. App.R. 9(B)(1), 9(B)(3), 9(B)(5)(b) and 10(A); Loc.R. 9.1. Appellant is required to file copy of the transcript order with the clerk of the trial court. Loc.R. 9(B). See Chart 2 for details on where to go to order a transcript of proceedings.
The Appellant is required to complete the record section of the docket statements to inform the court of the contents of the record.
Schedule and Calendar
Scheduling Order
After appellant files the notice of appeal and docket statement, the court of appeals will send to the parties to the appeal a scheduling order of events on the appeal. The scheduling order will set the due dates for filing the record and briefs. The scheduling order may be amended by the court or upon the request of a party in a motion. If the appellant fails, without good cause, to comply with the scheduling order, the appeal will be dismissed. App.R. 3; Loc.R. 3.3.
Regular or Accelerated Calendar.
The appeal will proceed on the Court’s regular or accelerated calendar depending on the complexity of the case and the wishes of the parties. If an appellant would like a case on the accelerated calendar, they may indicate such in the docket statement. The Court may also assign the appeal to its accelerated calendar at any time. App.R. 11; Loc.R. 11.1.
Transmission of the Record
The scheduling order will set the date for transmitting the record on appeal to the clerk of the Court of Appeals. It is the appellant’s obligation to do what is reasonably necessary to ensure that the record is timely transmitted to the Court of Appeals. App.R. 10(A); Loc.R 10(A).
A motion to extend the time for transmitting the record may be filed with the court of appeals by the appellant to ask for more time for the transcript of proceedings to be prepared or other parts of the record to be filed with the Court of Appeals. The Court of Appeals may grant that motion if the appellant can show good cause for the delay. App.R. 10(C); Loc.R. 10(B).
Motions
A motion seeking an order or other relief from the Court of Appeals must be in the form provided by the appellate and local rules. The motion must specify the relief sought, the grounds for that relief, and must be accompanied by a proposed entry granting the relief sought and any supporting papers required by the rules.
If filing in-person, the movant must file with the Court of Appeals the original and one copy of all motions. The motion and supporting papers must be served on all parties to the appeal.
A memorandum opposing a procedural motion may be filed only by leave of the Court. A memorandum opposing a substantive motion may be filed within 10 days of service of the motion. A reply in support of the substantive motion may be filed within 7 days of service of the opposing memorandum.
App.R. 15; Loc.R. 15.
Briefs
A brief is the written argument to the court of appeals by a party to an appeal.
- The brief of the appellant or cross-appellant states what errors they believe occurred in the lower court and why the court of appeals should reverse or modify the judgment appealed.
- The brief of the appellee or cross-appellee states why the court of appeals should affirm the judgment.
App.R. 16 and 19; Loc.R. 16.1.
Form 16.1 Sample Brief
App.R. 16, 18, and 19 and Loc.R. 16.1, 16.2, 18, and 19.1 set forth the requirements for a brief.
When preparing a brief, follow the rules and refer to the sample brief.
What does an appellate brief look like?
Format – A paper brief must be typed or prepared by a word processor (unless the court grants leave to file a handwritten brief), on 8½ by 11-inch paper. A brief filed electronically must be filed in searchable PDF format.
Style – The brief’s font must be at least 14-point and must be set in Times New Roman or Georgia typeface. Loc.R. 19(C). Text may appear on only one side of the paper and must be doubled-spaced, except that quotations more than three lines long may be indented and single-spaced, and headings and footnotes may be single-spaced. Margins must be at least one inch. Italics or underlining must be used for case names.
Length – In a regular-calendar case, the appellant and appellee briefs may not exceed 40 pages or 9,000 words, and the appellant’s reply brief is limited to 20 pages or 4,500 words. In an accelerated-calendar case, the appellant and appellee briefs may not exceed 20 pages, or 4,500 words and the appellant’s reply brief is limited to 10 pages, or 2,200 words. These page limits exclude the table of contents, certificate of service, and any appendices.
Cover The front cover of a brief must provide the following information:
- Name of the court of appeals and number of the case
- Caption of the case in the court below, with the appellant identified as such (including case number)
- Nature of the proceeding in the court of appeals (such as, whether it is an “appeal” or an action for a “writ”) and the name of the court below
- Title of the document (such as, “Brief of Appellant”)
- Name, email, and address of the party filing the brief
App.R. 19(A); Loc.R. 19.
What is included in an appellate brief?
Loc.R. 16.1 specifies what is required in a brief filed with the First District Court of Appeals. The Court of Appeals will strike any brief that does not substantially comply with App.R. 16 and Loc.R. 16.1, App.R. 19 or Loc.R. 19
Attachments to the Brief
- A copy of the final order that is being appealed must be attached to appellant’s brief. Loc.R. 16.1(A)(6).
- Copies of statutes, constitutional provisions, or cases are not to be attached unless they are not readily available on the internet. Loc.R. 16.1(E)
- Attachment of materials not in the record below are prohibited. Loc.R. 16(E).
- If a party attaches documents from the record to the brief, a table of contents and citation to the record must be included. Loc.R. 16.1(E).
Citations to the record References in a brief to the record on appeal are abbreviated,
- Transcript of proceedings: “T.p. [relevant page number].”
- Transcript of the docket and journal entries: “T.d. [document number assigned by the clerk of courts] at [page number within the document].”
App.R. 16(D); Loc.R. 16.1(D).
Citations to legal authority – Citations in a brief to a statute or a case must be provided in a form consistent with the Manual of Citations adopted by the Supreme Court of Ohio Reporter. The manual is available at http://www.supremecourt.ohio.gov/ROD/manual.pdf
Loc.R. 16(F).
When and how is a brief filed?
The scheduling order provides the dates for filing briefs. App.R. 18(A); Loc.R. 18.1(A).
Extending Time to File a Brief
For appeals on the regular calendar, a party may obtain a one-time automatic thirty (30) day extension of time to file a brief by filing a Notice of Automatic Extension of Time to File Brief. For appeals on the accelerated calendar, a party may obtain a one-time automatic fifteen (15) day extension of time to file a brief by filing a Notice of Automatic Extension of Time to File Brief. Notices must comply with the requirements set forth in Loc.R. 14(A). See Form 14.1 Notice of Automatic Extension.
Additional extensions are unlikely to be granted, but will be considered upon written motion supported by a showing of diligence and substantial need. Loc.R. 14(D). See Form 14D
If the brief is not filed on time or within the time as extended
If the appellant’s brief is not timely filed, the Court of Appeals may dismiss the appeal. If the appellee’s brief is not timely filed, the appellee may not be heard at oral argument, and the Court may accept as correct the facts and issues set forth in the appellant’s brief and grant the relief sought. App.R. 18(C)
Filing the brief
- The brief should be either filed with the court of appeal’s clerk or e-filed.
- The original of a paper brief cannot be bound or have dividers or tabs.
- The original and one copy of a brief must be filed, unless the brief is e-filed.
App.R. 18(B); Loc.R. 18.1(B) and 13.1(B).
Oral Argument
Oral argument is the spoken presentation to the Court of the arguments made by the parties in their briefs for or against affirming, reversing, or modifying the judgment appealed.
Who may argue?
The Court will hear argument by any party to the appeal who has filed a brief and has requested oral argument. Loc.R. 21(A). To request oral argument, the party must note “Oral Argument Requested” on the cover page of the party’s brief. The Court will not hear argument by:
- An incarcerated appellant who is self-representing;
- A party who has not filed a brief and has not been granted permission by the Court to argue;
- Any party, if the Court of Appeals determines that oral argument is not needed.
App.R. 18(C) and 21; Loc.R. 21(A).
When is argument?
Written notice will be provided to each party or the party’s counsel of the date, time, and place of oral argument, if oral argument is requested.
App.R. 21(B); Loc.R. 21.1(A) and (B)
Note: If oral argument is not requested or not permitted, the case will be submitted on the written briefs and the Court will notify the parties of the date in which the case will be submitted to a panel for decision
How long are arguments?
Each side has 15 minutes for oral argument.
- The time allotted to each side is shared if there are multiple appellants or appellees.
- The time may be extended by the court upon good cause shown in a motion filed within the time provided for filing the brief.
- Part of the time may be reserved by the appellant to respond to the appellee’s argument
App.R. 21(C); Loc.R. 21(F).
Where are arguments?
In-person oral arguments are held in the courtrooms for the First District Court of Appeals. The courtrooms are located on the 12th Floor of the William Howard Taft Law Center. In some instances, the Court will permit parties to argue remotely utilizing videoconferencing. To participate in oral argument in this manner, a party must file a motion with the Court. Loc.R. 21(E).
NOTE: The Court forbids the use of any electronic device or the display of real or demonstrative evidence during oral argument without prior approval. Loc.R. 21(H)-(I)
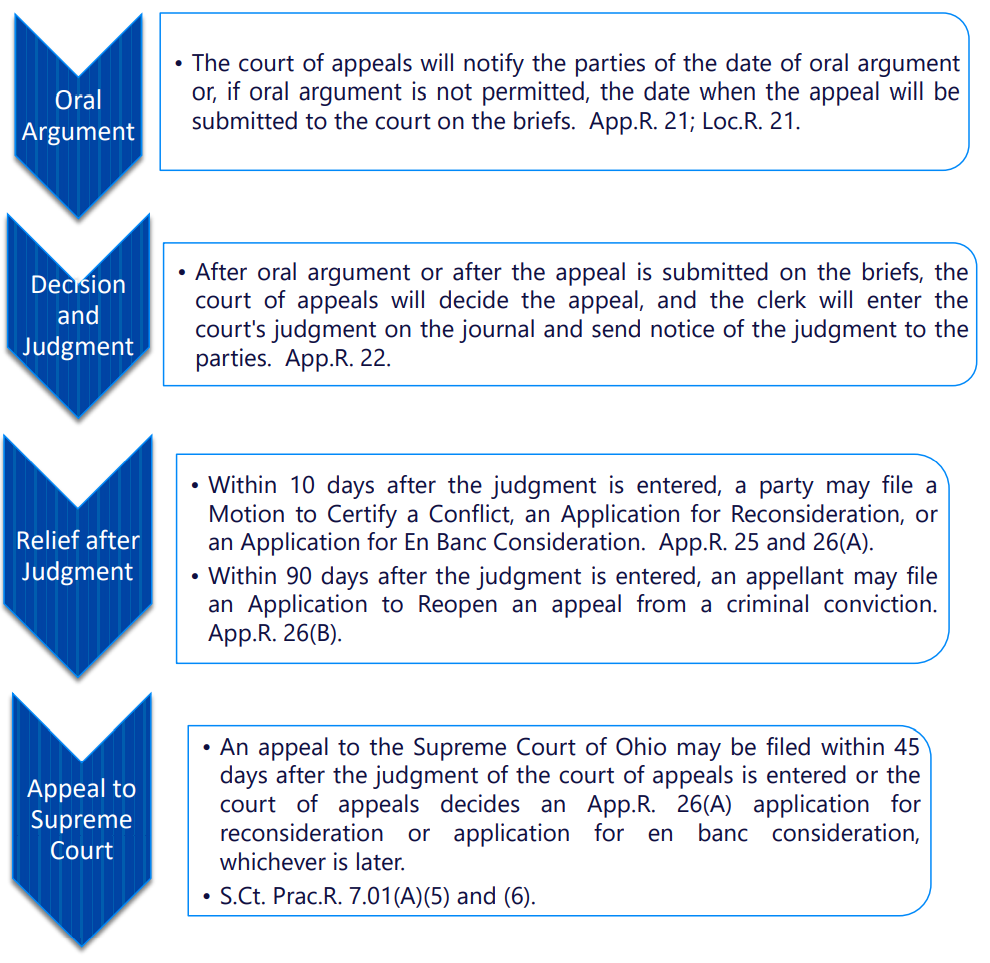
Decision and Judgment
After the appeal is submitted, either on the briefs or following oral argument, the Court will decide the appeal and file with the clerk its judgment affirming, reversing, or modifying the judgment appealed, or remanding the case to the court below for further proceedings. On that same day, the clerk will enter the judgment on the journal and notify the parties. The Court posts its decisions on Wednesdays and Fridays of every week on its website. The decisions can be viewed at www.firstdistictcoa.org.
A motion to stay the court of appeals’ judgment may be filed by any party to the appeal. App.R. 22, 27 and 30.
Relief after Judgment
A decision by the court of appeals may be challenged by filing the following:
Application for Reopening:
asking the Court of Appeals to reopen an appeal from a judgment of conviction in a criminal case, on the ground that the appellant was denied the effective assistance of counsel on appeal. The application must be filed within 90 days after the court’s judgment is journalized, unless the applicant can show good cause for not applying
within the 90 days. App.R. 26(B).
Application for Reconsideration:
asking the Court of Appeals to reconsider a judgment or order entered in the appeal, on the ground that the Court made an obvious error in the decision or did not consider, or did not fully consider, an issue that it should have considered in deciding the appeal. The application must be filed within 10 days after the judgment or order is journalized, unless the applicant can demonstrate extraordinary circumstances that would warrant enlarging the time. App.R. 26(A)(1) and 14(B). See Form 26
Application for En Banc Consideration:
asking that the Court’s judgment be vacated, and that the appeal be considered and decided by all six judges on the court of appeals, for the reason that the three-judge panel’s decision in the appeal conflicts with a prior panel’s decision on a dispositive issue. The application must be filed within 10 days after the three-judge panel’s judgment is journalized, unless the applicant can demonstrate extraordinary circumstances that would warrant enlarging the time. App.R. 26(A)(2) and 14(B).
Motion to Certify a Conflict,
asking the Court of Appeals to certify the record of the case to the Supreme Court of Ohio, for review and a final determination of a question decided by the Court that conflicts with the decision on that same question of law by the court of appeals for another district. The motion must be filed within 10 days after the judgment in the appeal is journalized, and that time may not be enlarged. App.R. 25.
Appeal to the Supreme Court of Ohio
If you wish to file an appeal of a First District Court of Appeals decision, please consult the Supreme Court Rules of Practice. Those rules can be found on their website at: https://www.supremecourt.ohio.gov/LegalResources/Rules/practice/rulesofpractice.pdf
Definitions
Affidavit of Indigency – A notarized form filed with the notice of appeal, affirming that the appellant is unable to pay for an appeal. Form 3.1.
Appeal – A review by a higher court of the proceedings in a lower court. App.R. 3, App.R. 4.
Appellant – The party who appeals a judgment.
Appellee – The party who defends a judgment.
Assignment of error – The statement in the appellant’s brief of how the trial court erred. App.R. 16(A)(3); Loc.R. 16.1(A)(3)(a).
Brief – The written argument filed with the Court of Appeals by a party to an appeal. App.R. 16-19; Loc.R. 16.1-19.1.
Citation – A reference to legal authority, such as a case or statute, or a reference to the record. App.R. 16; Loc.R. 16.1
Cross-Appeal – A second appeal filed by a party whose interests are not the same as the first appellant’s interests, but also wants the Court of Appeals to reverse or modify a part of the trial court’s judgment. App.R. 3(C).
Cross-Appellant – The party who files a cross-appeal. App.R. 3(C)(1).
Cross-Appellee – The party who opposes the cross-appellant’s cross-appeal (usually the appellant). App.R. 3(C)(1).
Docket Statement – A document required to be filed with the notice of appeal to assist the Court of Appeals in issuing a scheduling order by informing the Court of Appeals about the appeal, the order appealed, and what the record on appeal will contain. App.R. 3(G); Loc.R. 3.1.
Fee-Waiver Order – A court order waiving prepayment of the court costs or providing security for filing an appeal. R.C. 2323.311; Form 20 Civil Fee Waiver Affidavit and Order.
Indigent – A party to an action who is unable to prepay or pay for the fees or costs of the action or who is unable to employ counsel.
Motion – A written request for a court to make a specific ruling or grant some form of relief. App.R. 15; Loc.R. 15.1.
Notice of appeal – The document required to begin an appeal. App.R. 3(A) and 4; Loc.R. 3.1(A) and; Form 3.3NCR Notice of Appeal-Criminal and Form 3.3NCV Notice of Appeal-Civil.
Opinion – A written document filed with the judgment of the Court of Appeals, giving the Court’s reasons for its decision in the appeal. App.R. 12(A).
Oral argument – The in-court presentation by the parties or by counsel for the parties, providing reasons why the Court of Appeals should or should not affirm, reverse, or modify the trial court’s judgment or remand to the trial court for further proceedings. App.R. 21; Loc.R. 21.1.
Party – A person or entity who has a legal right to participate in an appeal.
Proof of service – A statement in a document filed with a court, certifying that the document was served on each party to a proceeding before the court and the method of service used. App.R. 13; Loc.R. 13.1.
Pro se – A party who appears before the court of appeals without a lawyer.
Record on appeal – The original papers and exhibits filed in the trial court, the transcript of the proceedings before that court, and the docket and journal entries that are transmitted to the Court of Appeals for its review of the judgment appealed. App.R. 9; Loc.R. 9.1.
Relief – The result a party seeks from the Court of Appeals in exercising its authority to affirm, modify, or reverse the judgment or order appealed. App.R. 12(A)(1)(a).
Reply brief – A brief filed by the appellant or cross-appellant to respond to arguments presented in the brief of the appellee or cross-appellee. App.R. 16 (C); Loc.R. 16.1(C).
Scheduling order – An order by the court of appeals setting the dates when the record and briefs are due to be filed. Loc.R. 3.3.
Stay – An order that puts the judgment appealed on hold until the Court of Appeals decides the appeal.
Standard of Review – The law that guides the Court of Appeals review in deciding an issue presented in the appeal. App.R. 16.1.
Transcript of proceedings – Part of the record on appeal that provides a written record of what happened at a trial or hearing during the proceedings leading to the judgment appealed. App.R. 9 and 10.
Transcript of the docket and journal entries – Part of the record on appeal that provides the papers filed and the entries made in the proceedings leading to the judgment appealed. App.R. 9.
Helpful Forms
Chart 1 – Where to file the notice of appeal
Chart 2 – Where to get the court reporter’s certification and order a transcript of proceedings
Checklist 1: Forms Needed to begin an Appeal (Civil)
Checklist 2: Forms Needed to begin an Appeal (Criminal)
Form 3.1A – Affidavit of Indigency
Form 3.1NCR – Notice of Appeal-Criminal
Form 3.1NCV – Notice of Appeal-Civil
Form 3.1DCR –Docket Statement – Criminal
Form 3.1DCV –Docket Statement – Civil
Form 3.4 – Motion to Appoint Counsel
Form 5 – Motion for Leave to File a Delayed Appeal
Form 7 – Motion for Stay
Form 9 – Motion for Preparation of Complete Transcript of Proceedings at State Expense
Form 13.2 – Personal Identifier
Form 14.1(A) – Notice Automatic Extension of Time Pursuant to Loc.R. 14
Form 14D – Motion to Extend Time
Form 16.1CR – Sample Brief—Criminal
Form 16.1CV – Sample Brief—Civil
Form 20 – Civil Fee Waiver
Form 26 – Application for Reconsideration
Form 28 – Motion for Voluntary Dismissal of Appeal


